Vyatta 6.2

Configure Vyatta(Core 6.2) as an OpenVPN server(in routing mode) using for the PKI part XCA instead of easy-rsa - - - In this paper we will configure Vyatta(Core 6.2) as an OpenVPN server(in routing mode) using for the PKI part XCA instead of easy-rsa. We will do so per my previous article. So first make sure you follow the steps from there in order to create a CA and issue certificates for the OpenVPN server and clients. Per the mentioned paper, I have prepared within a folder on a Windows 7 machine the following files: CA certificate, DH parameter file, client and server certificates, client and server private keys, see Figure 1: Figure1: XCA Exported Files Make sure the server's private key is in SSLeay compatible format, otherwise you may not be able to commit the configuration on Vyatta. The network diagram is presented in Figure2: Figure2: Network Diagram First simple configuration on the Vyatta machine(installed on hdd) to achieve basic connectivity. This was entered on the Vyatta machine: set interfaces ethernet eth0 address 192.168. Pipe Flow Advisor Crack. 22.234/24 set interfaces ethernet eth1 address 192.168.10.1/24 commit set service ssh protocol-version v2 commit save set protocols static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 192.168.22.1 commit edit service nat rule 20 set type masquerade set source address 192.168.10.0/24 set outbound-interface eth0 top commit save We need to copy on Vyatta the CA certificate, the server certificate, the server private key and the DH parameter file.
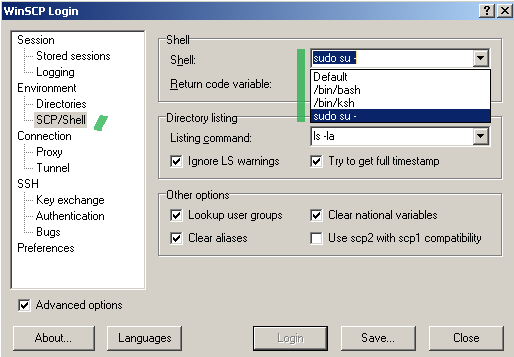
Per Vyatta's configuration guide Vyatta_BasicSystemRef_R6. C S R Prabhu Object Oriented Database Pdf here. 2_v01.pdf we can put these files within the /root location. There are a couple of ways to do this; I will use WinSCP. Note that, for example, the default administrator named vyatta is allowed to do sudo without being prompted with password. So if we configure WinSCP, per its, like in Figure3(use SCP and select the Advanced options) and Figure4(custom shell sudo su - on the SCP/Shell/ tab), we will be able to obtain write access to the /root location. Figure3: WinSCP use SCP Figure4: WinSCP custom shell For example, I've copied the above mentioned files like so on the Vyatta machine, see Figure5: Figure5: WinSCP Files copied on the Vyatta machine over SCP After we've copied these files on Vyatta, we can proceed and configure the OpenVPN server on it. We will enter a basic OpenVPN configuration on Vyatta, it will use UDP and listen for VPN connections on UDP port 1194(default OpenVPN port), we will assign IP addresses to the OpenVPN clients from the 192.168.200.0/24 subnet and we will push a route for the subnet behind Vyatta(192.168.10.0/24) to the OpenVPN clients in order for them to be able to reach resources located behind Vyatta over the VPN tunnel. Also we will use AES CBC 128-bit for data encryprion.